Research conducted by Kuldeep Kelkar and Jamie Yoo
In the #uxignite podcast, Jakob Nielsen encouraged the UX community to embrace Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning (AI/ML) to boost productivity. His pivotal advice was simple: “Start small, but start now.”
We observed User Researchers using ChatGPT
To understand the impact of AI on our workflows, we conducted a study with six user researchers employing ChatGPT for creating essential documents and artifacts for Competitive UX Benchmarking within the Health Insurance industry.
Document Types and Analysis
Participants (User Researchers) produced a variety of documents including Research Plans, Statements of Work, Screeners, and Moderator Guides. Beyond document creation, ChatGPT was instrumental in data analysis, theme identification from transcripts, and research report generation.
Insights Leading to Best Practices
The study revealed the value of structured, well-crafted prompts in achieving higher-quality outputs. Insights from this research have informed the development of a best practices framework, offering guidelines and practical examples to enhance ChatGPT’s utility in UX research.
Key Findings:
Crafting Effective Prompts: The study underscored the importance of precise prompts and structured inputs. Quality in, quality out.
Senior Researchers and ChatGPT: Experienced researchers demonstrated adeptness in prompt crafting, significantly enhancing productivity and artifact quality.
Rapid Growth for Juniors: Junior researchers, initially novices with AI, showcased remarkable productivity improvements following brief exposure to ChatGPT.
From Skepticism to Appreciation: Initially skeptical participants discovered unforeseen benefits and capabilities, turning apprehension into endorsement.
Prompting Best Practices: The R.E.F.I.N.E. Framework
Our findings indicate that the most effective prompts are those that are iterative and structured, ideally following the R.E.F.I.N.E. framework (Role, Expectations, Format, Iterate, Nuance, Example). This approach, coupled with the double diamond model of exploration and refinement, significantly improves output quality.
Example 1: Generating User Research Plan

Example 2: Unmoderated Study Build
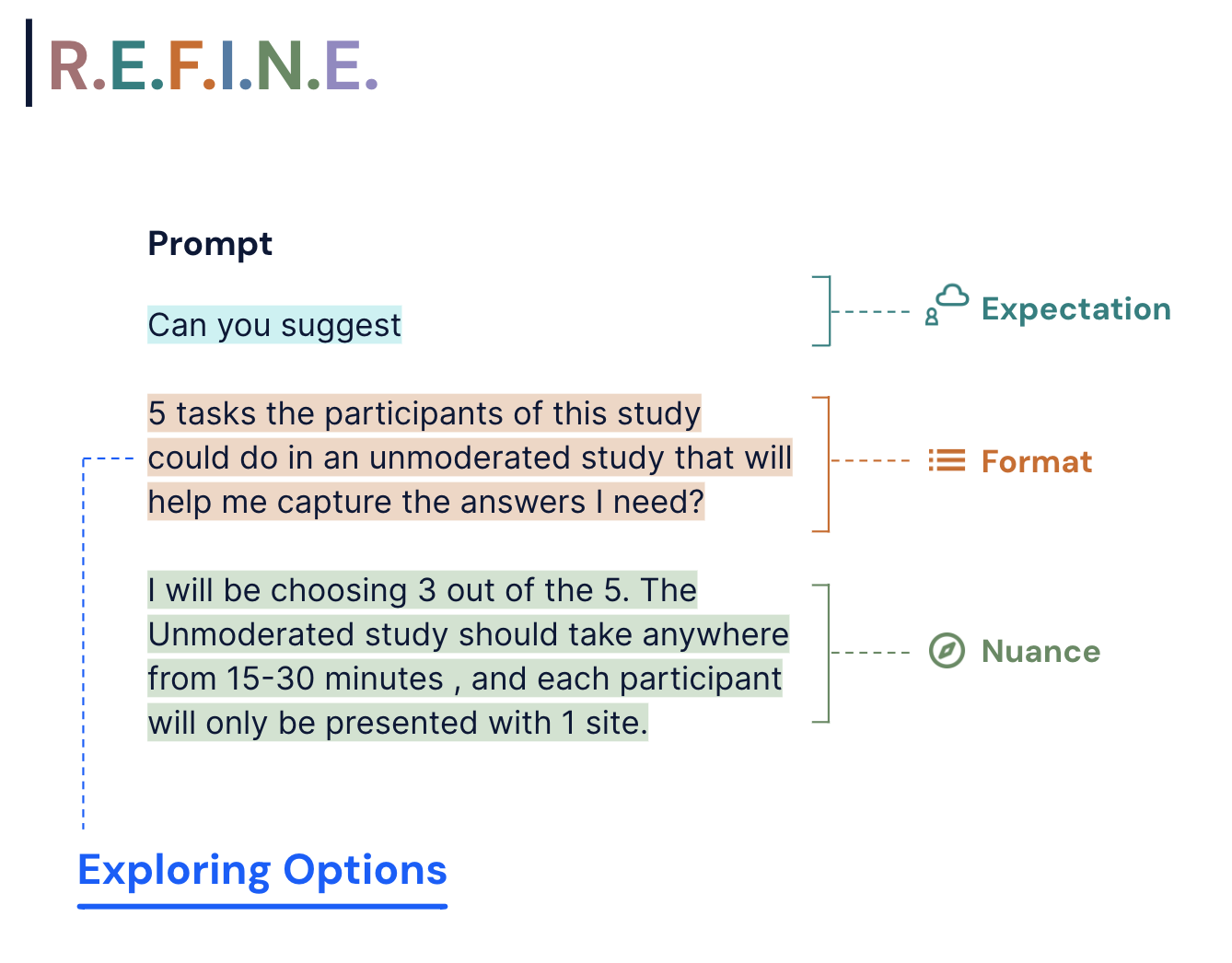
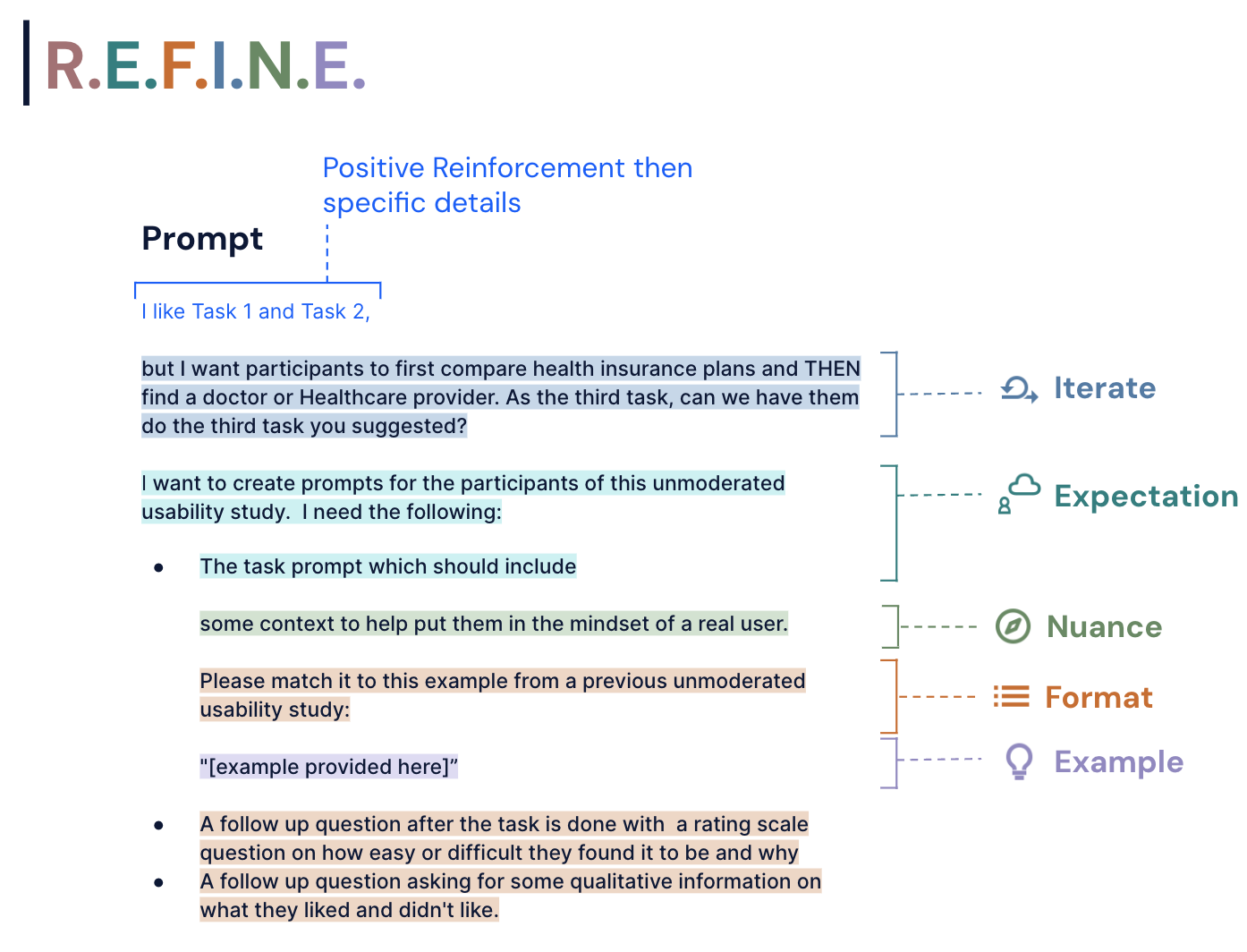
Things to note
Optimizing Prompts: By providing specific examples of research plans and instructing ChatGPT to follow a structured approach, we can gradually shorten the prompt chain over time.
Experimentation with CoPilot and Gemini: Our experiments with Microsoft CoPilot and Google Gemini yielded promising results.
Integration of AI/ML Models: In the near future, we anticipate seamless integration of AI/ML models into our daily tools such as MS Office, Google Suite, and User Research Tools. Consequently, a specialized standalone tool for Generative AI may become unnecessary.
Continued Importance of Prompt Engineering: Despite advancements, the iterative process of prompt engineering and adherence to the R.E.F.I.N.E. prompt structure will likely remain crucial for effective use of generative AI.
To do, next steps:
Try Our Examples for Yourself: Explore our illustrative examples and experiment with generative AI firsthand.
Start Small, Start Now: Start building your mental models, improve your prompting skills AI by taking small steps today.
Adhere to Company Policies: Always follow your company’s guidelines regarding the data that can or cannot be entered into ChatGPT, Co-Pilot, or Gemini.
—–
Examples shared above are from the Competitive UX Benchmarking research. Full report published on UXReactor website.
—-


